Immunization in Children - Pediatric OSCE Stations
Station 1- What is VVM and how will you interpret it?
Answer
 |
| How to interprete VVM |
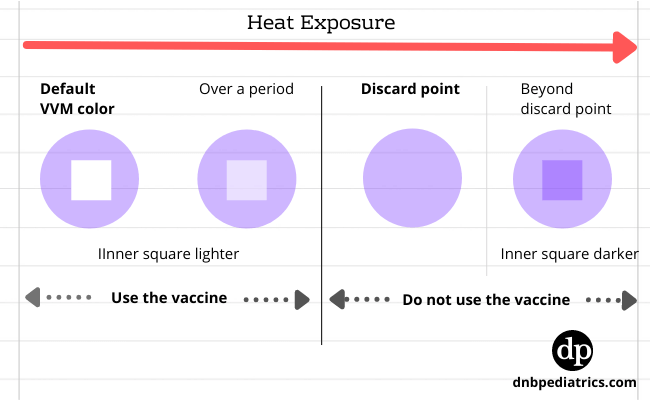
A vaccine vial monnitor (VVM) is a small label on a vaccine vial that changes color as the vaccine vial is exposed to heat. It gives a visual indication of whether the vaccine has preserved its potency.

|
| VVM on vials |
| Symbol | Explanation | Stage |
| 1 | The inner square is lighter than the outer circle. If the expiry date has not passed, use the vaccine | I |
| 2 | The inner square is darker but still remains lighter when compared to the outer circle. If the expiry date has not passed, use the vaccine | II |
| 3 | The color of the inner square and outer circle are the same, Do not use the vaccine. This is discard point | III |
| 4 | The inner square is, even more, darker than an outer circle, this is beyond the discard point. Do not use the vaccine. | IV |
Station 2- How do you store vaccines in the refrigerator?
Answer
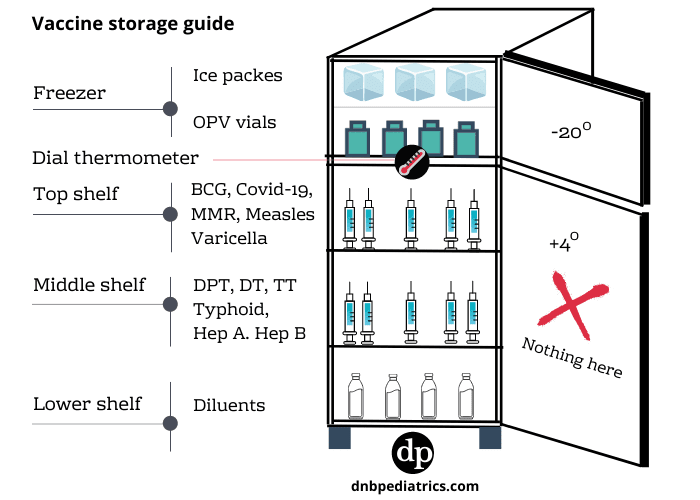
The following image illustrates the different storage compartments for common vaccines
 |
| How to store vaccines in a refrigerator - ref: WHO 2004 |
| Compartment | Vaccine |
| Freezer comprtament | OPV |
| Top shelf | BCG, Measles, MMR |
| Middle shelf | Tetanus, Diptheria, Pertussis, IPV, Hib, Combination vaccines, HPV, Typhoid, Hep A, PCV, influenza, rotavirus |
| Lower | Varicella |
Station 3- Name some contraindications and precautions for vaccination in general.
Answer
Contraindication to vaccination
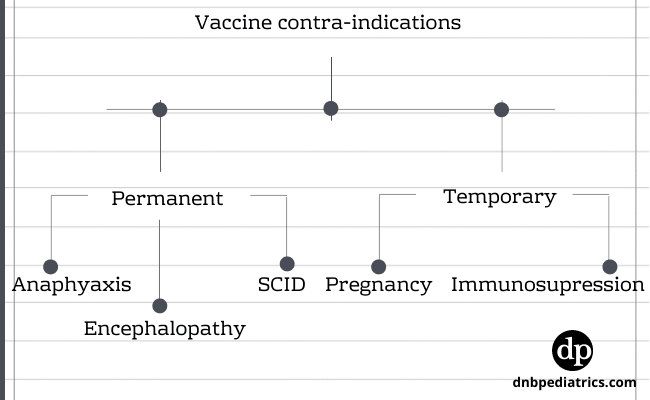
A contraindication is a condition in a recipient in which a vaccine, increases the chances of a serious adverse reaction that outweighs the therapeutic benefit. eg. - severe allergic reactions
|
| Contraindication to vaccination - ref IAP imm book 2018-19 |
Precaution
A Condition in the recipient that might increase the chance of serious adverse reaction or might compromise the ability of the vaccine to produce immunity.

|
| Precaution for vaccination of children - ref IAP imm book 2018-19 |
Station 4- What is a freeze watch indicator?
Answer
 |
| Freeze watch indicator for vaccines |
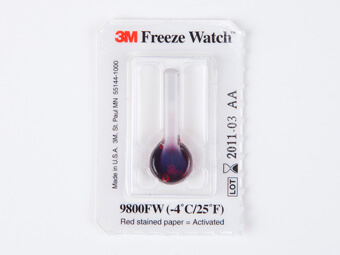
A freeze watch indicator is a small vial of red liquid attached to a white card and covered in plastic. Vial breaks if the temperature drops below 0 Celsius for >1 hour.
Freeze sensitive vaccines are
- Diphtheria.
- Tetanus.
- Pertussis.
- Liquid Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
- Hepatitis B.
Station 5- What are special vaccines you would advise for high-risk category children?
Answer
High-risk categories of children include
- Congenital or acquired immunodeficiency (including HIV)
- Chronic cardiac, pulmonary, hematologic, renal and liver disease
- Children on long term steroids, salicylates, immunosuppressive or radiation therapy
- Diabetes mellitus, CSF leak, Cochlear implant, Malignancies
- Children with functional/ anatomic asplenia/ hyposplenia
- Laboratory personnel and healthcare workers
- Travelers
Recommended vaccines for High-risk children
- Influenza Vaccine
- Meningococcal Vaccine
- Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine
- Cholera Vaccine
- Rabies Vaccine
- Yellow Fever Vaccine
- Pneumococcal vaccine (PPSV 23)
Station 6- An 11-year-old boy is adopted, no medical records are available and BCG scar is not seen. The adoptive parents want to know what vaccines have to be given. What will you advise?
Answer
- TDaP vaccine- single dose
- MMR- 2 doses at 4-8 weeks gap
- Hep B- 3 doses at 0,1 and 6 months
- Hepatitis A- 2 doses at 0, 6 months
- Typhoid- 1 dose every 3 years
- Varicella- 2 doses at 4-8 weeks
Station 7- About Influenza Vaccine
- What are the types of influenza vaccines in India?
- When is a Live Attenuated Influenza vaccine (LAIV) not recommended?
- What is IAP's recommended target prioritization for influenza vaccines?
Answers
Types of Influenza vaccine
Trivalent inactivated vaccines (TIV) and Live Attenuated Influenza vaccines (LAIV).
LAIV is not recommended in
LAIV is not recommended below 2 years of age, in high-risk individuals, and in pregnant women.
Target prioritization
- Elderly (> 65 years) / nursing-home residents
- HIV/AIDS, and pregnant women (especially to protect infants 0–6 months)
- Other groups: Health care workers, asthmatics, and children from ages 6 months to 2 years.
- Children, aged 2–5 years and 6–18 years, and healthy young adults.
Where 1 is the highest priority and 4 is the lowest priority.
Station 8- Regarding vaccination in symptomatic HIV cases, answers yes or no for the following
- Can BCG vaccine be given in symptomatic HIV cases
- Can OPV be given in symptomatic HIV cases
- Can measles, MMR and Varicella be given in symptomatic HIV cases
Answer
- No, BCG vaccine can not be given in symptomatic HIV cases
- Yes, if IPV is not affordable/available, OPV can be given in symptomatic HIV cases
- Yes, if CD4+ count > 15%, measles, MMR, and Varicella can be given in symptomatic HIV cases.
Station 9- Regarding BCG vaccination
- What solution is used to swab the site prior to BCG vaccination?
- When will you consider the BCG administration technique to be successful?
- What is the normal reaction at the vaccine site following successful vaccination?
- What condition is associated with BCG vial contamination?
Answer
- Normal saline or sterile water
- A wheal of 5 mm at the injection site
- A papule develops by 2-3 weeks, increases to a size of 4-8mm by 5-6 weeks, ulcerates and heals with scarring by 6-12 weeks
- Toxic shock syndrome
Station 10- Which is the Polio vaccine of choice for outbreak control? Which Polio vaccine type is more efficacious – Trivalent OPV or Bivalent OPV? What is enhanced IPV?
Answer
Polio vaccine of choice for outbreak control
OPV
More efficient OPV
Bivalent OPV is more efficacious than Trivalent OPV – as competition between different serotypes is eliminated
Enhanced IPV contains
- type 1 – 40 Ag U
- type 2 – 8 Ag U
- type 3- 32 Ag U
Station 11- What are the conditions that predispose to VDPV? Name the Polio serotypes more frequently associate with VAPP and VDPV
Answer
Conditions that predispose to VDPV are
a) Dropping immunization coverage
b) High population densities
c) Tropical conditions
d) previous eradication of wild poliovirus
Associated serotypes
VAPP – Type 2
VDPV – Type 3
Station 12- What is AEFI and when will you consider it serious? What are the different types?
Answer
AEFI is an adverse event following immunization
An AEFI is considered to be serious if it
- Results in death
- Develops life-threatening event
- Requires in-patient hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization
- Results in persistent or significant disability/incapacity
- Results in a congenital anomaly/birth defect or
- Requires intervention to prevent permanent impairment or damage.
Types of AEFI
1. Vaccine reaction
An event caused by the vaccine or precipitated by the vaccine when given correctly eg. VAPP after OPV
2. Programme error
An event caused by an error in vaccine preparation, handling, or administration. Egs- TSS after measles vaccine due to improper storage
3. Injection reaction
Event from anxiety about, or pain from the INJECTION, rather than the vaccine. Eg abscesses
4. Coincidental
An event that happens after immunization, but is NOT caused by it. Eg SIDS
5. Unknown
The cause of the event cannot be determined.
What are the recommended time limits for using vaccines after reconstitution?
Answer
- Varicella - 0 mins (and protect from light)
- MMRV - 30 mins (and protect from light)
- Yellow fever - 1 hour
- MEASLES/MMR - 4 to 6 hours
- Meningococcal PS vaccine -30 mins
- DTaP/Hib combination - 30 mins
Station 13- What is pre-exposure prophylaxis for rabies and for whom it is advised? What are the advantages of giving it?
Answer
PEP for rabies constitutes three doses of rabies vaccine to be given intramuscularly on days 0, 7 and 28
Pre-exposure prophylaxis for rabies is advised for
- Children having pets in the home
- Children perceived with higher threat of being bitten by dogs such as hostellers, risk of stray dog menace while going outdoor
- Veterinarians, those who work with animals
Advantages
In case of a dog bite, only two doses are to be given on days 0 and 3 and Rabies immunoglobulin (RIG) is not needed after receiving pre-exposure prophylaxis.
Station 14- Regarding Meningococcal Vaccine, What are the categories to be vaccinated as per IAP recommendations?
Answers
Following categories should be vaccinated with Meningococcal Vaccine.
- A.During disease outbreaks
- B. Vaccination of persons with high-risk conditions/situations
- Complement component deficiencies
- Functional/anatomic asplenia/hyposplenia
- HIV
- Healthcare workers exposed routinely to Neisseria meningitides
- Adjunct to chemoprophylaxis
- C. International travelers – Study abroad/ Hajj/ Sub-Sahara Africa
Station 15- What are the recent updates to the IAP Immunization schedule?
Answer
DTaP:
Preferably be avoided in primary vaccination series (at 6, 10 and 14 weeks)
IPV:
Instead of OPV at 6, 10, 14 weeks and 15 months, So OPV only at birth, 6 months, 9 months and 5 years
Hepatitis B vaccine:
The final (third or fourth) dose in the Hepatitis B vaccine series should be administered no earlier than age 24 weeks and at least 16 weeks after the first dose
MMR vaccine:
At 9 months and 15 months, No need for a booster at 5 years
Typhoid conjugate vaccine:
(TypBar) given at 9 to 12 months, with a booster at 2 years of age
Hepatitis A:
Single-dose for live attenuated H2-strain Hep-A vaccine
Two doses for all killed Hep-A vaccines are recommended at 12 months and 18 months
HPV:
- Only 2 doses of either of the two HPV vaccines for adolescent/pre-adolescent girls aged 9-14 years.
- For girls 15 years and older, and immunocompromised individuals 3 doses are recommended.
- For a two-dose schedule, the minimum interval between doses should be 6 months.
- For 3 dose schedule, the doses can be administered at 0, 1-2 and 6 months
1 comment
🩺 Help us refine this article — share corrections or additional information below. Let's elevate the accuracy of knowledge together! 💉💬